Businesses engaged in international trade need to navigate various taxes and duties. Customs duty in India is a key levy imposed on imported and exported goods. This guide explains the types of customs duties, the interplay with GST, refund mechanisms, and recent regulatory changes—all essential for importers and exporters aiming for compliance and cost efficiency.
What is customs duty?
Customs duty is a tax imposed by the federal government on goods entering or leaving India. While duty is payable at the time of import, exports enjoy duty-free status with a refund of duties paid on inputs. Goods are classified under the Harmonized System Nomenclature (HSN), which groups items by description, components, and use.
Trumps 2.0 imports tariffs
The U.S. announced a 26 percent tariff on Indian imports under President Trump’s reciprocal trade policy, targeting countries with large trade surpluses. The decision sparked concern in key Indian export sectors like textiles, agriculture, and gems and jewelry, though pharmaceutical exports were exempted.
Types of custom duties and taxes
When calculating customs duty, the following taxes are imposed:
|
Duty/charge |
Description |
Rate/note |
|
Basic Customs Duty (BCD) |
Charged on imported goods, either as a fixed amount (per unit) or based on the value (ad valorem), or both. |
Peak rate ~10% |
|
Social Welfare Surcharge |
Levied on the value of goods to support social welfare schemes. |
10% of the duty value |
|
Anti-dumping Duty |
Imposed if goods are imported at below fair market value, causing harm to local industries. |
Varies by product & origin |
|
Safeguard Duty |
Applied when a surge in imports threatens domestic industries. |
Temporarily imposed, varies |
|
Reciprocal Tariffs |
Tariffs imposed in retaliation to similar measures by other countries. |
Case-specific |
|
Customs Handling Fee |
Covers administrative costs of customs clearance. |
Typically, 1% of value |
|
Compensation Cess |
Applied on luxury or ‘sin’ goods such as SUVs, tobacco, aerated drinks. |
Product-specific (e.g., 15–22% on SUVs) |
|
Goods and Services Tax (GST) |
Imports attract Integrated GST (IGST), which is recoverable by businesses in the value chain. |
Same rates as domestic supply (0–28%) |
|
Integrated GST (IGST) |
Applied at the point of importation; ensures tax neutrality. |
Matches applicable GST slab |
How are imports and exports taxed under GST?
Who is liable to pay GST?
The importer of services will have to pay tax on reverse charge basis. But, in respect of import of online information and database access or retrieval services (OIDAR) by unregistered, non-taxable recipients, the supplier located outside India shall be responsible for payment of taxes, such as, OTT Platforms, Apple store, Google Store, etc.
For this purpose, either the supplier will have to take registration or will have to appoint a person in India for payment of taxes.
Under GST, the IGST replaces previous indirect taxes imposed on the import of goods and services. However, customs duty and other protective taxes such as anti-dumping duty, safe-guard duty continue to be levied on imports, in line with the previous tax regime.
Taxes on imports
The imports under GST are treated as inter-state supply; which means that IGST that is imposed on the inter-state supply of good and services is also imposed on the imports of goods and services. Since GST is a destination-based tax, IGST is levied in the State where the imported goods are consumed and import services are received. Import of services means the supply of any service when:
- Supplier of Service is located outside India;
- Recipient of services is located in India;
- Place of supply of services is in India;
- Payment in any currency whether in Indian Currency or in foreign exchange; and
- Transactions between establishments of same person also qualify as supply.
Import of goods
- Import of goods into India are deemed as inter-state supplies and accordingly subject to levy of IGST;
- Assessable value of the imported goods shall be determined as per the provisions of customs act and rules prescribed thereunder Custom Tariff Act;
- The assessable value of an article/product imported into India shall be increased by the amount of applicable custom duties and their respective cess; and
- IGST is then, levied and collected on amount computed as mentioned above.
Import of services
- Import of services under GST are subject to levy of IGST which is to be paid by the importer under Reverse Charge Mechanism.
- However, there is an exception to above, in case of import of OIDAR (Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval services) by an unregistered, non-taxable recipient. In this case a simplified procedure is prescribed for the suppliers outside India to take registration under GST in India and discharge the taxes.
|
Goods and Services Tax on Imports |
|
|
Import |
Taxes |
|
Import of Goods |
IGST + Basic Customs Duty + other protective duties (if applicable) |
|
Import of Services |
IGST |
Taxes on exports
Exports of goods and services are considered zero-rated supplies, meaning they are exempt from tax. For services, the export criteria include:
- The supplier being located in India and the recipient abroad.
- The place of supply and payment both occurring outside India.
- Payment received in convertible foreign exchange.
A Letter of Undertaking (LUT) allows GST-registered exporters to export without paying IGST, provided they commit to converting foreign exchange within a specified period.
Letter of undertaking (LUT)
The LUT is a document that GST-registered exporters can file to avoid paying Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) on their exports. Instead of paying taxes first and then claiming refunds later, exporters can simply submit an LUT and carry out tax-free exports.
Any business registered under GST can submit an LUT through Form GST RFD-11.
By filing an LUT, exporters provide an undertaking that they will fulfill all prescribed conditions under GST. This includes ensuring that payments for the exported goods or services are received in convertible foreign exchange or Indian rupees (where permitted by the RBI) within one year from the date of invoice issuance. If required, an extension can be granted as per government norms.
Essential documents for LUT
An LUT can be submitted by any individual who is registered under GST. Following documents are required for LUT:
- LUT cover letter - request for acceptance - duly signed by an authorized person;
- Copy of GST registration;
- PAN card of the entity;
- KYC of the authorized person/signatory;
- GST RFD11 form;
- Copy of the IEC code;
- Cancelled Cheque; and
- Authorization letter.
Deemed exports under GST
Certain domestic supplies are considered deemed exports, even though they do not leave India, and payment for such goods is received either in Indian rupees or in convertible foreign exchange. These supplies attract GST but qualify for a refund. Deemed Exports are also subject to levy of GST and are not zero-rated supplies, and such goods are also not eligible to be supplied under a Bond/LUT.
Refund of GST can be claimed either by the supplier or the recipient. The application for refund filed by the supplier or the recipient shall be considered only if neither party has been unjustly enriched during the course of the transaction.
Categories of goods notified as Deemed Exports:
- Supply of goods by a registered person against Advance Authorization given by the Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT);
- Supply of capital goods by a registered person against Export Promotion Capital Goods Authorisation;
- Supply of goods by a registered person to Export Oriented Unit; and
- Supply of gold by a bank or Public Sector Undertaking.
Refund of taxes under GST on account of zero-rated exports
- Refund of IGST paid on export of goods:
- Eligibility: All conditions of zero-rated supplies are met;
- Refund application: No refund application is required to be filed separately as the Shipping Bill/Bill of export filed is deemed as refund application;
- Time limit for claiming refund: No specified time limit prescribed under the law due to automatic nature of refund process; and
- Eligible documents for verification of claim by the Department: The shipping details entered by the assessee along with the invoicing details while filing GSTR-1 are received by the customs portal for verification of claim. Filing of valid GSTR-3B return is necessary to substantiate the payment of IGST on export of goods.
- Refund of accumulated input tax credit balance in case goods/services are exported without payment of tax under Bond/LUT:
- GST paid on input by exporters in the course of domestic sale may be claimed;
- Refundable amount shall be sanctioned within 60 days from the date of receipt of application; and
- Except for certain notified categories, 90 percent of the claim amount will be refunded provisionally within seven days from the date of acknowledgement, subject to final assessment of claim.
Blocked credit
Blocked credit under GST refers to goods and services for which tax credit cannot be claimed as per legal provisions. If a registered person uses goods or services for both business and personal purposes, they can only claim credit for the portion used for business.
Input tax credit shall not be available in respect of the following:
- Food and beverages, outdoor catering, beauty treatment, health services, cosmetic and plastic surgery except where an inward supply of goods or services or both of a particular category is used by a registered person;
- Membership of a club, health and fitness centre;
- Rent-a-cab, life insurance and health insurance;
- Travel benefits extended to employees on vacation such as leave or home travel concession; and
- Goods or services or both used for personal consumption.
Input tax credit offset mechanisms
|
|
IGST Liability |
CGST Liability |
SGST Liability |
|
IGST |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
CGST |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
SGST |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
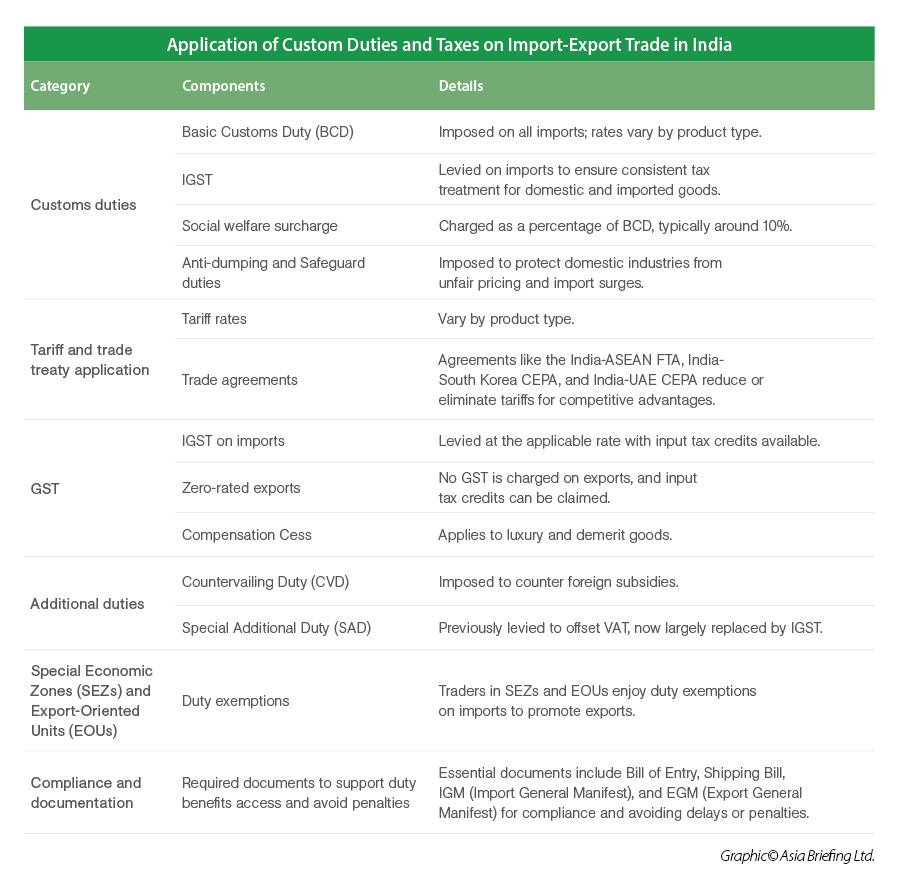
Custom duty rates
Electronics industry and precious metals
|
Particulars |
Rates |
|
Mobile phone, mobile PCBA and chargers |
15% |
|
Gold and silver |
6% |
|
Gold and silver dore |
5.35% |
|
Platinum |
6.4% |
|
Broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimp and fish feed |
5% |
|
Coins of precious metals |
6% |
|
Platinum and Palladium used in the manufacture of noble metal solutions, noble metal compounds and catalytic convertors |
5% |
|
Flat panel detectors (including scintillators) and X-ray tubes for use in manufacture of X-ray machines for medical, surgical, dental or veterinary use |
5% 10% |
|
Specified parts for use in a manufacturing of connectors |
Nil |
|
Oxygen Free Copper for use in manufacture of Resistors |
Nil |
|
Specified capital goods for use in manufacture of solar cells or solar modules, and parts for manufacture of such capital goods |
Nil |
|
Components and consumables for use in manufacture of specified vessels |
Nil |
|
Technical documentation and spare parts for construction of warships |
Nil |
|
Goods under S. No. 404 of Notification No. 50/2017 Customs, used for petroleum exploration operations |
Goods under S. No. 404 of Notification No. 50/2017 Customs, used for petroleum exploration operations |
|
Interactive Flat Panel Displays (IFPDs) |
20% |
|
Open Cell and related components |
5% |
Source: India Budget 2025-26
Critical goods
|
Custom Duties Exemption for Critical Goods |
|||
|
Commodities |
Unwrought Metals & Powders |
Waste & Scrap Metals (Tariff Reduced to Nil, Effective 1st May 2025) |
Unwrought; Waste and Scrap; Powders of: |
|
Natural Graphite |
Unwrought Tin |
Antimony, waste & scrap |
Gallium |
|
Natural sands |
Unwrought tungsten, including bars and rods obtained simply by sintering |
Beryllium, waste & scrap |
Germanium |
|
Quartz (other than natural sands); quartzite |
Unwrought molybdenum, including bars and rods obtained simply by sintering |
Waste & Scrap of Bismuth and Bismuth Alloys |
Indium |
|
Strontium sulphate (natural ore) |
Unwrought tantalum, including bars and rods obtained simply by sintering, powders |
Cadmium, waste & scrap |
Niobium |
|
Copper ores and concentrates |
Cobalt, unwrought |
Cobalt, waste & scrap |
Vanadium |
|
Cobalt ores and concentrates |
Bismuth, unwrought |
Molybdenum, waste & scrap |
|
|
Tin ores and Concentrates |
Unwrought zirconium powders |
Rhenium, waste & scrap |
|
|
Tungsten Ores and Concentrates |
Unwrought antimony powders |
Tantalum, waste & scrap |
|
|
Molybdenum ores and concentrates |
Beryllium unwrought powders |
Tungsten, waste & scrap |
|
|
Zirconium ores and concentrates |
Hafnium unwrought |
Zirconium, waste & scrap |
|
|
Hafnium Ores and concentrates |
Rhenium unwrought |
||
|
Vanadium ores and concentrates |
Cadmium unwrought powders |
||
|
Niobium or tantalum ores and concentrates |
Cadmium, wrought |
||
|
Antimony Ores and Concentrates |
|||
|
Tellurium |
|||
|
Silicon, containing by weight not less than 99.99 percent of silicon |
|||
|
Other silicon |
|||
|
Selenium |
|||
|
Alkali or alkaline earth metals, rare-earth metals, scandium and yttrium, whether or not intermixed or inter-alloyed |
|||
|
Silicon dioxide |
|||
|
Potassium hydroxide |
|||
|
Oxides, hydroxides, and peroxides of strontium or barium |
|||
|
Cobalt oxides |
|||
|
Cobalt hydroxides |
|||
|
Commercial cobalt oxides |
|||
|
Lithium oxide and hydroxide |
|||
|
Vanadium oxides and hydroxides |
|||
|
Natural Graphite |
|||
|
Molybdenum oxides and hydroxides |
|||
|
Antimony Oxides |
|||
|
Cadmium oxide |
|||
|
Chlorides of Nickel |
|||
|
Strontium chloride |
|||
|
Sulphates of Nickel |
|||
|
Nitrates of potassium |
|||
|
Lithium carbonates |
|||
|
Strontium carbonate |
|||
|
Salts of oxometallic or peroxometallic acids of Beryllium and Rhenium |
|||
|
Compounds, inorganic or organic, of rare earth metals |
|||
|
Bismuth citrate |
|||
|
Artificial Graphite, colloidal or semi-colloidal graphite, preparations based on graphite or other carbon in form of pastes, blocks, plates, or other semi-manufactures |
|||
|
Source: Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) |
|||
Medical industry
Customs duties are exempt on three additional cancer medications—Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, and Durvalumab. Additionally, duties on x-ray tubes and flat panel detectors for medical x-ray machines have been reduced under the Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP). PMP aims to boost domestic production of medical x-ray machines and their sub-assemblies, enhancing local value addition.
AiMeD's pre-budget memorandum to the Finance Ministry emphasizes the need to monitor the maximum retail price (MRP) of imported medical devices to ensure affordability for Indian consumers. AiMeD believes that the reduction of import duties is not benefiting consumers, as they are still paying significantly more than the landed price due to inflated MRPs. They advocate for the withdrawal of concessional duty notifications and the implementation of a 5 percent – 15 percent duty on medical device imports.
|
Particulars |
Rates |
|
Medicines/drugs/vaccines supplied free by United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Red Cross etc. |
Nil |
|
Drugs and materials |
Nil |
|
Specified goods imported by accredited press cameraman |
Nil |
|
Specified goods, imported by accredited journalist |
Nil |
|
Capital goods, raw materials and spares for repairs of ocean-going vessels |
Nil |
|
Spare parts and consumables for repairs of ocean-going vessels registered in India. |
Nil |
|
Lifesaving medical equipment for personal use |
5 |
|
Life-Saving drugs like Keytruda etc. |
Nil |
|
Lifesaving drugs/medicines for personal use |
Nil |
|
Additional Life‑saving Drugs |
36 additional drugs fully exempt; 6 drugs at 5% duty |
|
Patient Assistance Programs (PAP) |
Exemptions extended to 37 additional medicines; 13 new programs incorporated |
|
Archaeological artefacts for exhibition in a museum |
Nil |
|
Specified raw material for sports goods |
Nil |
Source: India Budget 2025-26
Leather and textiles industry
|
Particulars |
Revised rate 2025-26 |
|
Raw hides and skins or raw skins (excluding raw hides of buffalo) |
40% |
|
Raw hides and skins of buffalo |
30% |
|
Tanned or crust hides and skins of bovine (including buffalo) or equine animals, other than E.I. tanned leather |
20% |
|
Tanned or crust skins of sheep or lambs, other than E.I. tanned leather |
20% |
|
Tanned or crust hides and skins of other animals, other than E.I. tanned leather |
20% |
|
E.I. tanned leather |
Nil |
|
Finished leather of goat, sheep and bovine animals and of their young ones |
Nil |
|
Raw furskins |
40% |
|
Tanned or dressed furskins |
20% |
|
Wet Blue Leather |
Fully exempt |
Source: CBIC
Others
The BCD on non-biodegradable and hazardous PVC flex banners has been raised from 10 percent to 25 percent to discourage their import.
|
Particulars |
Rates |
|
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flex films (flex banners/sheets) |
25% |
|
Garden umbrellas |
20% or INR 60 per piece, |
|
Laboratory chemicals (HS code 9802) |
10%* |
|
Other roasted nuts and seeds, including such areca nuts |
30% |
|
Other nuts, otherwise prepared or preserved, including such areca nuts |
30% |
|
Tinned copper interconnect for manufacture of solar cells or solar modules |
5% |
|
Solar glass for manufacture of solar cells or solar modules |
10% |
|
Carrier‑grade Ethernet switches |
10% |
|
* The Ministry imposes a 10 percent Basic Customs Duty on most laboratory chemicals under HS code 9802, except for undenatured ethyl alcohol. Additionally, there has been a significant increase in customs duty on imported lab chemicals, raising it from 10 percent to 150 percent. |
|
Source: India Budget 2025
Export-import procedures in India
Businesses planning to set up a trading company, or start importing or exporting from India, must understand the stages and stakeholders involved in the process, as well as the regulatory framework and documentation required.
In India, the imports and exports are regulated by the Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992, which empowers the federal government to make provisions for development and regulation of foreign trade. The current provisions relating to exports and imports in India must be read alongside the new Foreign Trade Policy 2023, which follows the Foreign Trade Policy of 2015-2020.

Export-import documentation in India














